
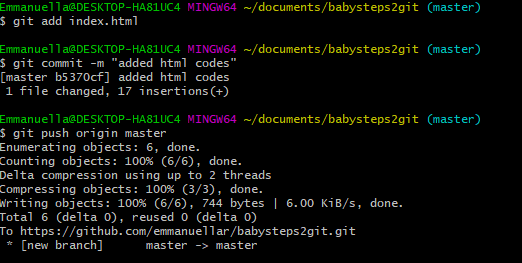
Coming back, let's see the two already installed editors with Git. In this course we will be using Notepad++ as the text editor with Git. It should be noted by you that choosing your editor is your personal choice and you should use an editor with which you are comfortable and have been using for a while. The options also appeared during the installation to which we agreed and installed those editors. Default Text Editors with Git Bashįor the ease of developers, there are two editors already included with the Git Bash.
USING GIT BASH TUTORIAL WINDOWS
For this you have many choices including some pre-installed editors and it is recommended to use Notepad++ on a windows machine. For the same purpose, we require a text editor to work our way around along with many more features. This way it is very hard to write a particular message in a terminal like Command Prompt or Git Bash. For example pressing enter is automatically meant that you are executing the written command. Each terminal has its own protocols and it behaves accordingly. You must be knowing that a terminal (Command Prompt, Git Bash, etc) only accepts the pre-defined commands and executes them. You must have worked previously on the terminal for anything. The answer to this question is very similar. Set Up Notepad++ for Git Bash in Windows.So we need to set these things only once ( in case you won't change it further). The commands we execute changes the global configuration file and the settings are saved permanently in the configuration file. As described earlier, these are just a one time set up. Now we are ready to set a few more things in this tutorial. The direct commit will perform both actions for us.In the previous tutorials, we have Set Up our defaults credentials to Git config. In intellij we can also commit files directly without adding them to staging first. Let's add the file to stagging and then commit. Let's make some changes to our previously committed Java file. The committed files' color will change to the default color: Making changes to versioned files Now Files from 'Default changelist' will disappear.
USING GIT BASH TUTORIAL CODE
Also if you don't want to 'perform code analysis' and 'check TODO', uncheck those options (they are checked by default):Ĭlick on 'commit'. Right click on the selected files to commit:Įnter commit message. Or we can also use right click>Git>Add as shown:Īfter adding, the file color has changed to green (green is for newly added staged file).
Right click on the selected files to add them to staging as shown: Nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track) Nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to MINGW64 /d/git-with-intellij-example (master) Let's confirm that from git-bash: MINGW64 /d/git-with-intellij-example (master) The above color (red) shows that Main.java file is unversioned (untracked). In Intellij, each file has its own status marked with a specific color, check out this for color-to-status listing. ignore, can be used which has a various useful functionality for creating/editing. gitignore file manually at the project's root:Īs seen in 'Local Changes' tab, all Intellij specific files disappeared and their color in the 'Project' tree view also turned to normal color.Ī plugin called. We will not use this view and will create. gitignore file, but it maintains an internal Intellij file for ignoring artifacts. Ignoring FilesĪbove view does not create. Open View>Tool Windows>Version Control(Alt+9):Īs seen above 'Local Changes' tab shows all untracked files in red color.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
